These are challenging times. But in every crisis, lies great opportunity. This special call for papers seeks to promote learning at such a difficult time. The idea is to create teaching cases that develop learning and discussion in class about how the world and businesses can react to profound changes. The scientific community has assembled spaces for discussion on how this crisis affects teaching and business, but we need long lasting resources for teaching how to manage future crisis to come. … Read More →
The Importance of Scientific Publications in Times of Pandemic Crisis [Originally published in Clinics, vol.75]
Though we are accustomed to the concept of scientific evidence that is preferably based on large clinical trials that take years to complete, we must now rely on case studies, single cohort studies, and even the opinions of experts. However, we know that we cannot lose sight of the criteria for evidence-based medicine, and must remember to evaluate all potential biases existing in this type of scientific information without limiting its dissemination. … Read More →
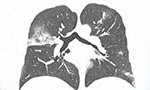
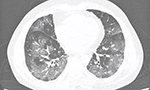
Presentation of pulmonary infection on CT in COVID-19: initial experience in Brazil [Originally published in J. bras. pneumol., vol. 46 no. 2]
The disease caused by the new coronavirus spread to all continents, and is now classified as a pandemic. Given the magnitude achieved, scientific interest in COVID-19 has also grown in the international literature, including its manifestations on imaging studies, particularly on CT. To date, no case series have been published in Brazil. Therefore, our objective was to describe the CT findings in an initial series of twelve patients. … Read More →
Personality differences and COVID-19: are extroversion and conscientiousness personality traits associated with engagement with containment measures? [Originally published in Trends Psychiatry Psychother.]
In December 2019, an outbreak of the novel coronavirus, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) probably occurred in Wuhan, China. By March 2020, the WHO had declared a pandemic. Containment measures such as social distancing and hand hygiene were recommended. In this study, we start from the hypothesis that engaging with containment measures in a pandemic situation should be more comfortable for some people than for other people. Thus, individual differences should be associated with engagement with containment measures. … Read More →
How should health systems prepare for the evolving COVID-19 pandemic? Reflections from the perspective of a Tertiary Cancer Center [Originally published in Clinics, vol.75]
In light of the emerging data, we discuss issues to be considered as health systems systematize their responses. We are not trying to predict the future, but rather, present potential scenarios. Herein, we provide the perspective of the ICESP, a publically funded tertiary referral cancer center in Brazil. The current editorial does not represent institutional or governmental positions. Formal policies take time to receive official approval. … Read More →
Nonpharmaceutical interventions for tackling the COVID-19 epidemic in Brazil [Originally published in Epidemiol. Serv. Saúde, vol. 29 no. 2]
In the absence of prior immunity in the human population and with no vaccine against SARS-CoV-2, its highly virulent nature means that case numbers grow exponentially. Nonpharmaceutical interventions are indicated in this context, aimed at inhibiting transmission between humans, slowing the spread of the disease and consequently reducing and delaying the peak of its occurrence on the epidemiological curve. … Read More →
Schizophrenia and COVID-19: risks and recommendations [Originally published in Braz. J. Psychiatry]
“Is my son at risk in view of COVID-19?” A patient’s mother contacted our Schizophrenia Outpatient Clinic as soon as news about the coronavirus pandemic reached Brazilian headlines. I immediately remembered how we hear in mental health services that “patients with severe mental illness are immune deficient.” But is this true? What are the implications of the COVID-19 pandemic for schizophrenia patients and their families? … Read More →
Physically Active Lifestyle as an Approach to Confronting COVID-19 [Originally published in Arq. Bras. Cardiol.]
Considering the recommendations for social isolation currently imposed in different countries, it is fundamental to encourage the population to maintain a physically active lifestyle routine as a preventative health measure during this period of confronting the spread of the virus. During periods of confinement at home, the population tends to adopt a sedentary routine, which favors increased body weight gain, as well as the emergence of comorbidities associated with greater cardiovascular risk, in addition to psychosocial disorders. … Read More →
Tuberculosis and coronavirus: what do we know? [Originally published in Epidemiol. Serv. Saúde, vol. 29 no. 2]
As we celebrate World Tuberculosis (TB) Day on March 24th and as we draw close to the first milestone, in 2020, of the World Health Organization’s new tuberculosis control strategy, known as the End TB Strategy, it is fitting to examine the dimensions of the TB situation in Brazil in times of the COVID-19 pandemic, the agent of which is coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. … Read More →
SciELO Preprints begins operations
The SciELO Program has launched the SciELO Preprints server – https://preprints.scielo.org – with the aim of accelerating the availability of research articles and other scientific communications before, or in parallel with, their evaluation and validation by scientific journals through the peer review process. Although open to all thematic areas, SciELO Preprints will focus on immediately serving communications related to COVID-19. … Read More →
COVID-19 in Brazil: advantages of a socialized unified health system and preparation to contain cases [Originally published in Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. vol. 53]
Even before the first COVID-19 cases were identified in Brazil, the country had articulated several measures ranging from the creation of ordinances and laws, to isolation and quarantine. However, the number of cases has increased significantly, requiring new measures, mainly to reduce mortality and worsening of cases. A socialized unified health system (UHS) and the fact that countries in Latin America were among the last ones with reported COVID-19 outbreaks have contributed to anticipated actions. … Read More →
Translating transmissibility measures into recommendations for coronavirus prevention [Originally published in Rev. Saúde Pública, vol. 54]
The rapid increase in clinical cases of the new coronavirus disease, COVID-19, suggests high transmissibility. However, the estimates of the basic reproductive number reported in the literature vary widely. Considering this, we drew the function of contact-rate reduction required to control the transmission from both detectable and undetectable sources. Based on this, we offer a set of recommendations for symptomatic and asymptomatic populations during the current pandemic. Understanding the dynamics of transmission is essential to support government decisions and improve the community’s adherence to preventive measures. … Read More →
Structured thoracic computed tomography report for COVID-19 pandemic [Originally published in Einsten, vol. 18]
We have observed an increase in requests of chest computed tomography (CT) since the first records of cases in Brazil. It is crucial to highlight that the definite diagnosis of COVID-19 is made by RT-PCR, and a normal chest CT does not rule out diagnosis. However, currently, the RT-PCR result has taken longer than CT reports to be available, so CT has taken an important role in a comprehensive assessment of patients for demonstrating high sensitivity (although low specificity), to detect the most frequent pulmonary findings of the disease. … Read More →
Assessing the severity of Covid-19 [Originally published in Epidemiol. Serv. Saúde, vol. 29 no. 2]
The fourth update of the Pandemic Influenza Plan prepared by the US Department of Health and Human Services, from 2017, included measures for different government and civil society areas. In addition, in order for the response to be proportional to the severity of the situation, it uses the Pandemic Severity Assessment Framework as a risk assessment tool, proposing two assessment dimensions: transmissibility and clinical severity. … Read More →
Science during the pandemic [Originally published in Cad. Saúde Pública, vol.36 no.4]
Various scientific journals in Brazil have published studies on the impact of primary healthcare (PHC) on the population’s health, including in identifying the limits and conditions for improvement in the current context. However, rather than improving the PHC proposal, there have been mass layoffs. Scientists have also decried the underfinancing of SUS, including the impacts of a fiscal austerity policy that has cut essential budget funding from the social and health areas. … Read More →





















Recent Comments