Preparedness is crucial to reduce the health, economic, and social impacts of a future epidemic, it is also the only way to avoid the spread of other diseases. Pandemics are not aleatory events but are the consequence of human interactions with the environment and could be avoided or reduced through science and investments in health, education and transportation and improved through better conditions of living. Image: Lizzie Mayorga. … Read More →
COVID-19 and acute pulmonary embolism: what should be considered to indicate a computed tomography pulmonary angiography scan? [Originally published in Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop., vol. 53]
Here, we present a case of a patient with COVID-19 who developed acute pulmonary embolism. Clinical and laboratory data and findings of non-enhanced CT indicate possibility of acute pulmonary embolism, and support the decision to proceed with computed tomography pulmonary angiography that can objectively identify filling defects in pulmonary arterial branches. Image: Martha Dominguez de Gouveia. … Read More →
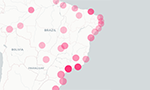
Spatiotemporal evolution of coronavirus disease 2019 mortality in Brazil in 2020 [Originally published in Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop., vol. 53]
In summary, Brazilian states with the greatest lack of health resources have shown the highest COVID-19 mortality rate. Inequalities in availability and access to the health care system represent additional challenges, given the increase in COVID-19 mortality in the country. This study reinforces the need for an urgent expansion of the operational capacity of the Unified Health System.
Image: Veit Hammer. … Read More →
War economy and the COVID-19 pandemic: Inequalities in stimulus packages as an additional challenge for health systems [Originally published in Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop., vol. 53]
War economics refers to the set of exceptional economic measures taken during a certain period of time, generally defined by the existence of an armed conflict (war). It is characterized by the increase in public spending and centralization of economic guidelines within the scope of public power, which starts to dictate the economy’s mode of operation seeking to save it. War economics refers to the set of exceptional economic measures taken during a certain period of time, generally defined by the existence of an armed conflict (war). It is characterized by the increase in public spending and centralization of economic guidelines within the scope of public power, which starts to dictate the economy’s mode of operation seeking to save it. Image: newelement. … Read More →
Individuals with covert severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection: Are they a critical booby-trap? [Originally published in Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop., vol. 53]
I believe that in Egypt, the first phase of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic was characterized by symptomless (covert) carriers. Covert carriers are individuals who test positive for the virus on laboratory testing but are symptomless and can shed the virus. Numerous researchers assume that there is an unobserved pool of these carriers because in many cases, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections could not be related to contact with persons with infection or to travel to epidemic areas. … Read More →
Clinical characteristics and therapeutic procedure for a critical case of novel coronavirus pneumonia treated with glucocorticoids and non-invasive ventilator treatment [Originally published in Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop., vol. 53]
The novel coronavirus pneumonia (NCP) outbreak occurred in Wuhan, China at the end of 2019. Here, we report the clinical characteristics and therapeutic procedure for a case of severe NCP. The patient was started on glucocorticoids and non-invasive ventilator treatment. After treatment, the patient’s symptoms improved, and the status was confirmed as NCP negative. Our results may provide clues for the treatment of NCP. Image: Adhy Savala. … Read More →
Surveillance of the first cases of COVID-19 in Sergipe using a prospective spatiotemporal analysis: the spatial dispersion and its public health implications [Originally published in Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop., vol. 53]
We performed a prospective space-time analysis using confirmed cases of COVID-19 during the first 7 weeks of the outbreak in Sergipe. The prospective space-time statistic detected “active” and emerging spatio-temporal clusters comprising six municipalities in the south-central region of the state. The Geographic Information System (GIS) associated with spatio-temporal scan statistics can provide timely support for surveillance and assist in decision-making. Image: Brian McGowan. … Read More →
New Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): advances to flatten the curve the prison population [Originally published in Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. vol. 53]
To respond to this crisis, we need to consider prisons as reservoirs that could lead to resurgence of the epidemic if it not adequately addressed. The interrelationship between prison-system health and public health is a global reality, with several countries presenting their successful experiences in facing the pandemic in the prison system. Available in English. Image: Sigmund. … Read More →
Importation and early local transmission of COVID-19 in Brazil, 2020 [Originally published in Rev. Inst. Med. trop. S. Paulo, vol. 62]
We conducted the genome sequencing and analysis of the first confirmed COVID-19 infections in Brazil. Rapid sequencing coupled with phylogenetic analyses in the context of travel history corroborate multiple independent importations from Italy and local spread during the initial stage of COVID-19 transmission in Brazil. Available in English. Image: engin akyurt. … Read More →
Is Brazil prepared for the new era of infectious disease epidemics? [Originally published in Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. vol. 53]
In Brazil, the Unified Health System (SUS) plays the main role in the preparation of the country for this new era. SUS has been acting in the response to the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) even before the identification of the first case in Latin America, with the declaration of national public health emergency. Available in English. … Read More →
COVID-19 in Piauí: initial scenario and perspectives for coping [Originally published in Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical vol. 53]
In Piauí, a state located in northeastern Brazil, the first suspected case of COVID-19 was reported on February 27, 2020. The first case was confirmed on March 19, 2020, and until the March 31, there were a total of 18 confirmed cases and 4 deaths due to COVID-19, with a fatality rate of 22.2%; two of these deaths occurred in Teresina, the capital of Piauí, where most of the confirmed cases are concentrated (16/18). Available in English. … Read More →
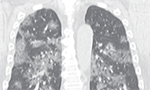
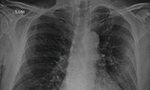
COVID-19 – Computed tomography findings in two patients in Petrópolis, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil [Originally published in Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. vol. 53]
High-resolution chest CT is the most effective radiological examination for the early detection of lung involvement by COVID-19. The largest sample study to date has shown that, among 3,665 confirmed cases, in 95.5% (n = 3,498) of the patients, pulmonary impairment was correctly diagnosed by CT, which provides valuable information for diagnosis and evaluates the severity of lung disease caused by COVID-19, guiding clinical treatment. Available in English. … Read More →
COVID-19 in Brazil: advantages of a socialized unified health system and preparation to contain cases [Originally published in Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. vol. 53]
Even before the first COVID-19 cases were identified in Brazil, the country had articulated several measures ranging from the creation of ordinances and laws, to isolation and quarantine. However, the number of cases has increased significantly, requiring new measures, mainly to reduce mortality and worsening of cases. A socialized unified health system (UHS) and the fact that countries in Latin America were among the last ones with reported COVID-19 outbreaks have contributed to anticipated actions. … Read More →
Driving forces for COVID-19 clinical trials using chloroquine: the need to choose the right research questions and outcomes [Originally published in Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. vol. 53]
Chloroquine was unequivocally demonstrated to have in vitro inhibiting effects on SARS-CoV-2 infection and was precociously publicized as having a beneficial effect in COVID-19 patients after a study conducted in Marseille, France showed a viral load reduction in COVID-19 patients. Since there is no specific antiviral therapy for coronavirus infections to date, the announcement of partial and fragile data led to precipitated political manifestations by major government leaders and contributed to uncoordinated recommendations of the drug to severe patients. … Read More →
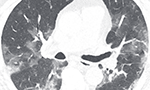
Chest radiography and computed tomography findings from a Brazilian patient with COVID-19 pneumonia [Originally published in Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. vol. 53]
A 73-year-old man was admitted to the emergency department with a 4-day history of fever, chills, dry cough, and fatigue. He had arrived in São Paulo, Brazil, on the preceding day. His symptoms had begun when he was traveling in northern Italy with 12 friends, three of whom had been diagnosed with COVID-19. He reported having systemic arterial hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. … Read More →




















Recent Comments