El informe Situación de la enfermería en el mundo 2020: invertir en educación, empleo y liderazgo, lanzado por la Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS) el 7 de abril de 2020 proporciona una visión y una agenda prospectivas para las políticas relacionadas con esta profesión, al tiempo que el mundo celebra en 2020 el Año Internacional de los Profesionales de Enfermería y Partería y enfrenta la pandemia de enfermedad por coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19). Disponible en español. Imagen: Luke Jones. … Read More →
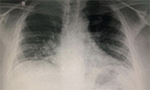
The trauma and acute care surgeon in the COVID-19 pandemic era [Originally published in Rev. Col. Bras. Cir., vol. 47]
Immediate measures must be taken to guarantee access to safety equipment throughout the country, since all trauma victims and/or patients with emergency surgical conditions must be treated as potential carriers of COVID-19. Image: Paul Felberbauer. … Read More →
Physical Exercise in Patients with Heart Disease and in the General Population in Times of Coronavirus [Originally published in Arq. Bras. Cardiol.]
What is most important is to emphasize that physical inactivity in a treacherous enemy. Its effects typically do not manifest in an acute manner as is the case with SARS-COV-2, whose effects need to be combated with emergency health measures based on the best scientific evidence. Image: Josh Calabrese. … Read More →
The Heart and COVID-19: What Cardiologists Need to Know [Originally published in Arq. Bras. Cardiol.]
The cardiovascular complications evidenced in patients with COVID-19 derive from several mechanisms, ranging from direct viral injury to complications secondary to the inflammatory and thrombotic responses to the infection. The proper care of patients with COVID-19 requires special attention to the cardiovascular system aimed at better outcomes. Image: Alexandru Acea. … Read More →
Coronavirus and the Heart | A Case Report on the Evolution of COVID-19 Associated with Cardiological Evolution [Originally published in Arq. Bras. Cardiol.]
Case report of a patient with diabetes mellitus who contracted the novel coronavirus in community, evolved with cardiac disorders and died. … Read More →
COVID-19: Updated Data and its Relation to the Cardiovascular System [Originally published in Arq. Bras. Cardiol.]
In turn, it is believed that there is a relationship between COVID‑19 and damage to the heart muscle, and hypertensive and diabetic patients, for example, seem to have worse prognosis. Therefore, COVID‑19 may worsen in individuals with underlying adverse conditions, and a not negligible number of patients hospitalized with this virus had cardiovascular or cerebrovascular diseases. Image: Jesse Orrico. … Read More →
Older adults living under social distancing: possibilities for tackling Covid-19 [Originally published in Rev. bras. geriatr. gerontol. vol. 23, no. 2]
Therefore, the concerns of the group must be disseminated among all parties who debate issues related to the older population that receives treatment through primary health care, allowing them to provide guaranteed care for this population during the pandemic caused by the new coronavirus, and contributing to a new approach to the care model for this age group in Brazil. Available in English. Image: Max Bender. … Read More →
COVID-19 The challenges and opportunities for qualitative articles [Originally published in Rev. Bras. Saude Mater. Infant., vol. 20, no.1]
Of all these moments, it exploded from the beginning a great number of researches thats ought to determine not only the biological and epidemiological mechanisms but the clinical features, in which led patients and their family members to over crowd care centers specialized in the field. Itis clear that these epidemics also represent issues to be faced by the governments, and further more, no one can forget these family members and people’s emotional suffering. Image: jesse orrico. … Read More →
Eficácia da máscara facial (TNT) na população para prevenção de infecções por coronavírus: Revisão sistemática
Como indicado para o benefício potencial das máscaras padrão TNT. Para o cenário atual de pandemia por COVID 19, recomenda-se a educação sobre o uso adequado de máscaras, relacionadas a medidas individuais de proteção. Disponível em português. … Read More →
Recommendations of the Brazilian College of Surgeons for laparoscopic surgery during the COVID-19 pandemic [Originally published in Rev. Col. Bras. Cir., vol. 47]
The aim of this technical note is, trough a compilaton of publications and recommendations from Scientific Societies of Surgery worldwide, to provide guidelines regarding laparoscopic access during the COVID-19 pandemic. Image: Arseny Togulev. … Read More →
Laparoscopic or robotic intraoperative management to minimize aerosol dispersion: Adaptations to the context of the COVID-19 pandemic [Originally published in Rev. Col. Bras. Cir., vol. 47]
In this publication, we highlight and teach adaptations to be made with commonly used materials in laparoscopy to help prevent the spread and contamination of the healthcare team assisting surgical patients. Image: Piron Guillaume. … Read More →
Alternatives for establishing a surgical airway during the COVID-19 pandemic [Originally published in Rev. Col. Bras. Cir., vol. 47]
Currently, the states with the highest number of cases are, respectively, São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Distrito Federal and Ceará. The objective of this work is to offer alternatives in order to guide surgeons regarding the surgical management of the airways in patients with suspicion and / or confirmation for COVID-19 infection. Image: Tim Cooper. … Read More →
Physical Activity And Reducing Sedentary Behavior During The Coronavirus Pandemic [Originally published in Arq. Bras. Cardiol.]
Based on the studies consulted, the evidence confirms the importance of continuing to practice physical activities during the novel coronavirus pandemic, with light to moderate intensity and duration, preferably in outdoor environments or at home. In addition, it is also very important to emphasize reducing sedentary behavior, namely, time spent sitting, lying down, or reclining, excluding sleep hours, and time spent in front of the television, computer, and similar devices. Image: Izuddin Helmi Adnan. … Read More →
Immunocompromised patients and coronavirus disease 2019: a review and recommendations for dental health care [Originally published in Braz. Oral Res., vol. 34]
Changes in the current guidelines have been proposed to SARS-CoV-2 infection control in order to provide the best and safe dental practice. However, they still need to be validated by future studies. Available in English. Image: Jon Tyson. … Read More →
The need to strengthen Primary Health Care in Brazil in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic [Originally published in Braz. Oral Res., vol. 34]
Brazil, like other countries, has faced the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. As Brazil has a universal and decentralized health system, in which PHC has been the model of health re-organizing the health system; here we reflected the importance of strengthening PHC in Brazil in the times of coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. Available in English. Image: Tim Mossholder. … Read More →




















Recent Comments